Ingrown hairs, a common yet often painful issue, occur when hairs grow sideways or curl back into the skin, leading to redness, inflammation, and possible infection. This detailed guide aims to shed light on the nature of ingrown hairs, explore their causes, and introduce a variety of effective strategies for both prevention and treatment.
Deciphering the Phenomenon of Ingrown Hairs
Characterized by the sideways growth or curling back of hair into the skin due to clogged follicles with dead skin, ingrown hairs are a widespread concern. Although anyone can suffer from ingrown hairs, those with curly or coarse textures are more prone, especially in areas subjected to regular hair removal like the face, neck, underarms, legs, and bikini line.
Root Causes of Ingrown Hairs
The act of hair removal, whether through shaving, waxing, or plucking, stands as the chief culprit for ingrown hairs. The type of skin, particularly oily or thick, may further predispose individuals to this condition by facilitating follicle clogging. Additionally, tight garments and friction can aggravate the situation, trapping hairs under the skin.
Strategies to Forestall Ingrown Hairs
Adopting correct hair removal practices is pivotal in averting ingrown hairs. Employing a sharp razor, shaving in the hair growth direction, and using a gentle shaving cream are key. Exfoliation plays a vital role in eliminating dead skin and ensuring proper hair growth. Selecting hair removal products that align with your skin type can also significantly reduce irritation.
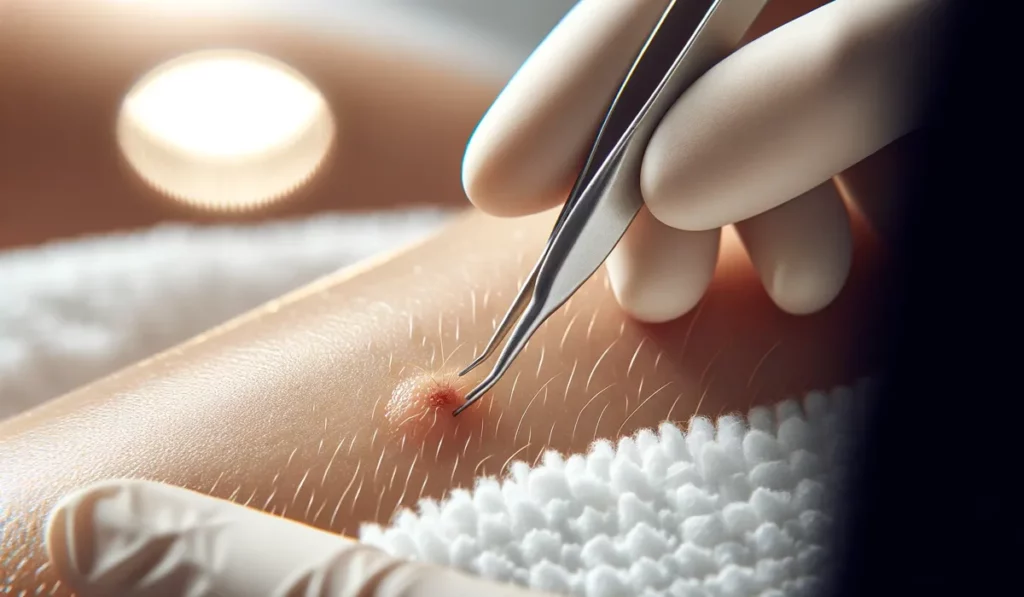
Eradicating Ingrown Hairs
For those grappling with ingrown hairs, an array of home-based and clinical solutions are available.
Home-Based Remedies for Ingrown Hairs
Applying warm compresses can soften the skin, facilitating the emergence of the hair. Sugar scrubs can mildly exfoliate the skin, whereas essential oils like tea tree offer antiseptic benefits to diminish inflammation and avert infections.
Clinical Interventions for Ingrown Hairs
Techniques such as laser hair removal and electrolysis present more permanent answers by curbing hair growth and lessening ingrown hair occurrences. Chemical peels are effective in exfoliating dead skin and preventing follicle blockages.
Pharmacy Solutions
Applying creams with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can mitigate inflammation and address infections in ingrown hairs. Products designed for exfoliation and serums to prevent ingrown hairs are specifically formulated to stop hairs from growing inward.
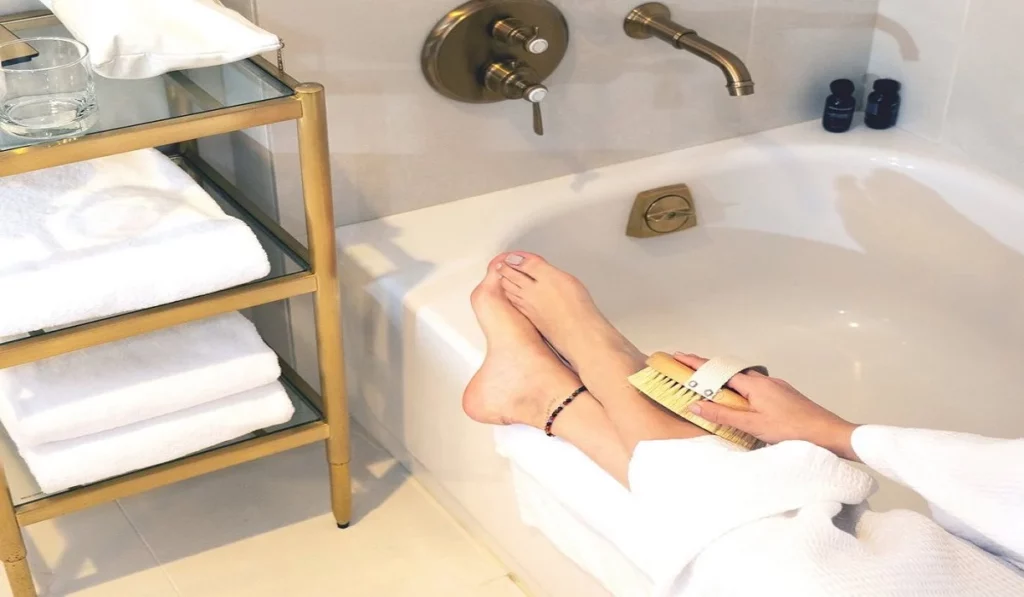

Importance of Exfoliation
Consistent exfoliation is crucial in warding off ingrown hairs by clearing dead skin that can ensnare hairs. Both manual and chemical exfoliants prove beneficial, yet selecting a suitable type for your skin to avoid irritation is essential.
Post-Removal Care and Skin Recovery
Post-extraction, maintaining cleanliness and hydration in the affected area is vital. Steer clear of tight-fitting clothes to reduce friction and irritation. Using a soothing balm or lotion can aid in healing and forestall future ingrown hairs.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Should signs of infection like pus, severe discomfort, or fever arise, seeking medical counsel is crucial. Persistent ingrown hairs that defy home-based treatments may necessitate professional care.
Although ingrown hairs are bothersome, adopting appropriate preventative measures and treatments can lead to smooth, trouble-free skin. Whether through at-home remedies, clinical treatments, or over-the-counter products, grasping the origins and proper skin care is fundamental in the prevention and management of ingrown hairs.
- What triggers the occurrence of ingrown hairs?
- How does one prevent ingrown hairs post-shaving?
- What are some natural treatments for ingrown hairs?
- What is the recommended frequency for exfoliation to avoid ingrown hairs?
- Could ingrown hairs evolve into more severe skin issues?
- What constitutes the most effective method for ingrown hair removal?








